Cemetery GPR Scanning? A Brief Guide!
Cemetery GPR Scanning – what is it? GPR stands for Ground Penetrating Radar. This technology allows us to scan the ground to see what is hidden beneath the surface. It’s a non-invasive method of detecting objects buried deep in soil, sand, or gravel.
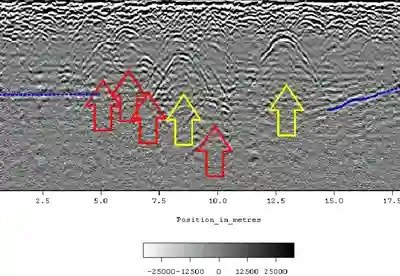
Archaeologists and other scientists use cemetery GPR scanning to detect structures, objects, and even human remains in an area the naked eye cannot see.
One of the most popular uses of GPR scanning in the cemetery industry is to find unmarked graves or graves without headstones. GPR scanning allows for rapid identification of these graves without disturbing the environment or causing harm to anyone who works on site.
Why should you care about Cemetery GPR Scanning?
Because it can help you find unmarked graves and identify human remains, which are often the most important part of a burial site, many people want to be buried next to family members. Still, if the person was buried in an unmarked grave or if their remains were moved from an original burial plot, it may be difficult for family members to find their loved one’s final resting place.
GPR scans can also be used to determine whether or not bones have been disturbed by root growth or ground movement over time—which can happen when trees grow over old cemeteries and cause damage to the remains.
What is GPR?
Using ground penetrating radar, or GPR, you can locate underground anomalies like concealed objects, water or utility lines, and unmarked burial sites without disturbing the ground. To make scans and find underlying elements, these radar devices fire a series of pulses over a predetermined area (say, a part of a graveyard).
GPR is a safe and reliable surveying tool for sensitive locations since it examines areas of interest without digging, excavating, or upsetting the ground. It can be used to find groundwater tables, air pockets, voids, subterranean pipes, geological features and changes in the strata, concrete, metal, plastic, and PVC materials.
Finding unmarked graves with GPR
GPR, commonly known as ground penetrating radar, is a non-intrusive sub-surface imaging technology. It offers a very thorough visual profile of what is beneath the surface. GPR services are ideal for detecting burial vaults, unmarked graves, and buried headstones. Ground Penetrating Radar Mapping Services are excellent for determining lost or available cemetery space, markings that have relocated, and coffin location. Additionally, Ground Penetrating Radar Services will provide a composite sitemap identifying grave sites, placements, and depth for cemeteries with lost or destroyed burial records.
Adding GPR findings to your cemetery maps
Even ancient cemeteries use contemporary technology. GPR results can be simply entered into your online database if your cemetery uses management software with digital maps. By incorporating this information, cemeteries may see in real-time which plots are taken up or blocked, which ones have been sold, and which ones are still open.
The GIS cemetery mapping team at ViaVista Mapping works with cemeteries to analyze GPR scans and pinpoint the precise GPS positions of unidentified burials, headstones that have been buried, and other abnormalities. The GIS cemetery mapping team then fills historical record gaps by adding this information to each cemetery’s online map.
What distinguishes seismic reflection from GPR?
GPR operates under similar principles to seismology. The primary distinction is that ground-penetrating radar detects subterranean structures using electromagnetic energy rather than the acoustic energy of seismic waves.
Seismology refraction surveys capture signals that refract through the earth and return to the surface. These acoustic waves are bent back towards the surface by an increase in seismic velocity in the ground, which is connected to the elastic characteristics and density of the earth. Seismic imaging is frequently used to map horizontal structures below the surface, although it is less useful for identifying vertical features.
Learn more about our GPR services HERE.
Find more information about preserving cemeteries.
Contact us today find out more about our services and for a free quote.
